One-Dimensional Array
Suppose, you need to store student number of 100 students. Will you define 100 variables?
int y1, y2,…., y100;
An Array is an indexed data structure to represent several variables having the same data type:
int y[100];
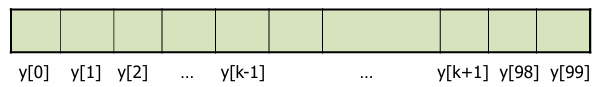
Array
- An array is a sequenced collection of same types of variabels. Each variables (or element) has an index.
- Each room of array is called cell.
- Index uniquely refers to a value stored in a cell.
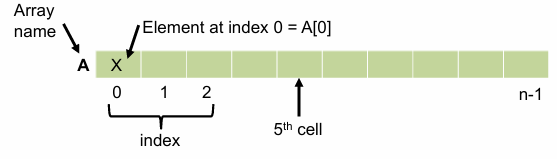
Array in memory
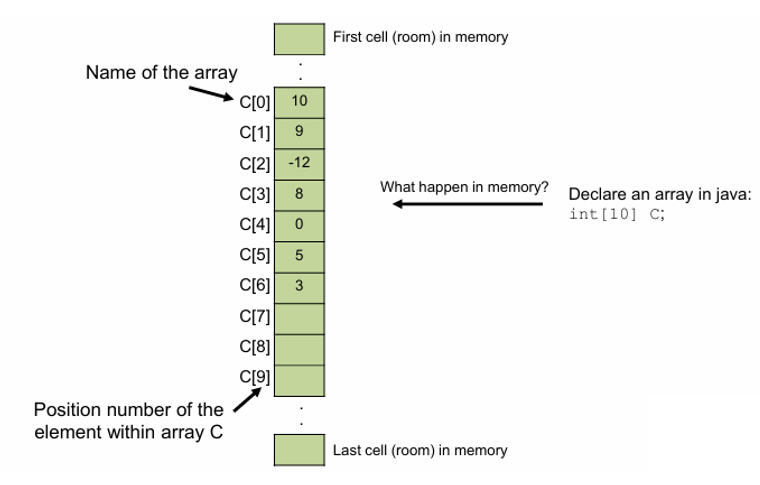
Array Length and Capacity
- Array has a constant length. the length of array shows the maximum number of things could be stored in the array, which is sometimes called capacity.
- In Java, the length of array is determined by the syntax A.length.
- Any value of array is accessible by A[index]
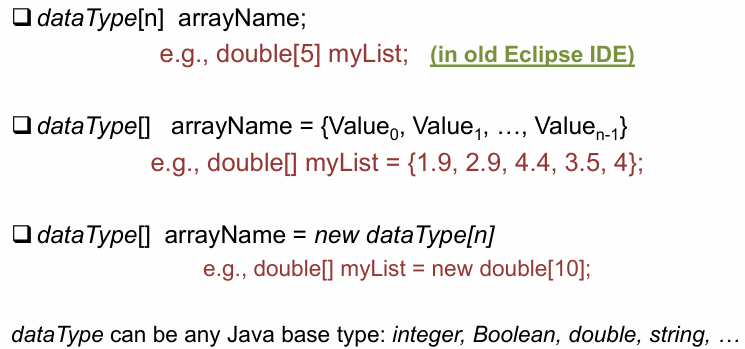
Declaring Arrays in Java
Processing Arrays
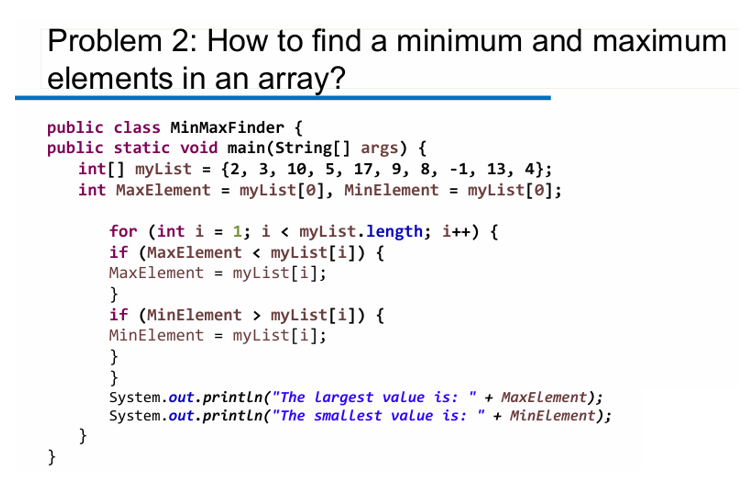
We often use for loop, for eachloop, if (then else) because the size of the array is known and all the rooms have same type.

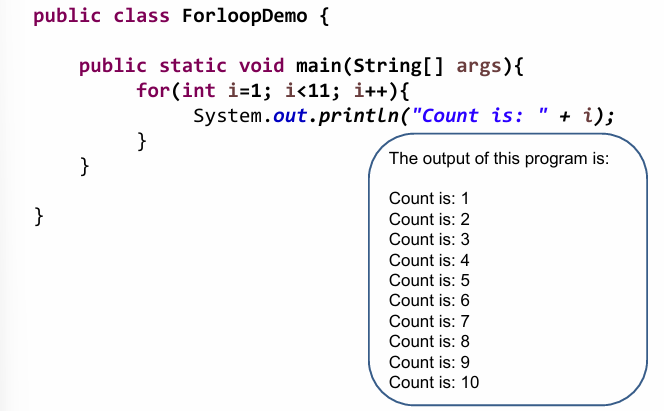
For loop Java sample



Drawbacks of Array
Define the array length in prior: consume memory’ space in advance.
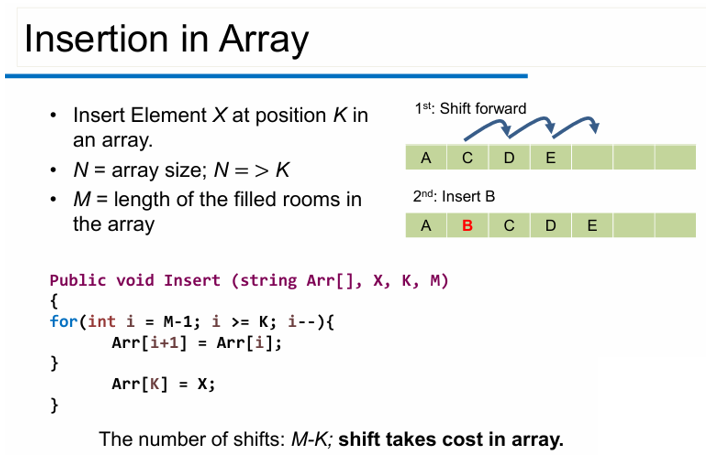
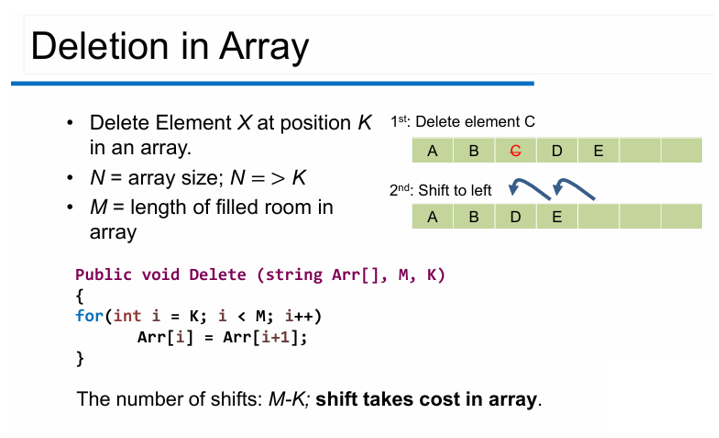
Shift: inserting or deleting just one element in the middle of the array (note: not in the last room) is computationally expensive.

Summary
- A quick revision for key Java concepts.
- Introduced Array and Matrix
- Discussed advantages and disadvantages of
array data structure - Explained several examples to implement Array
and Matrix in Java
*** End of Part 2 ***