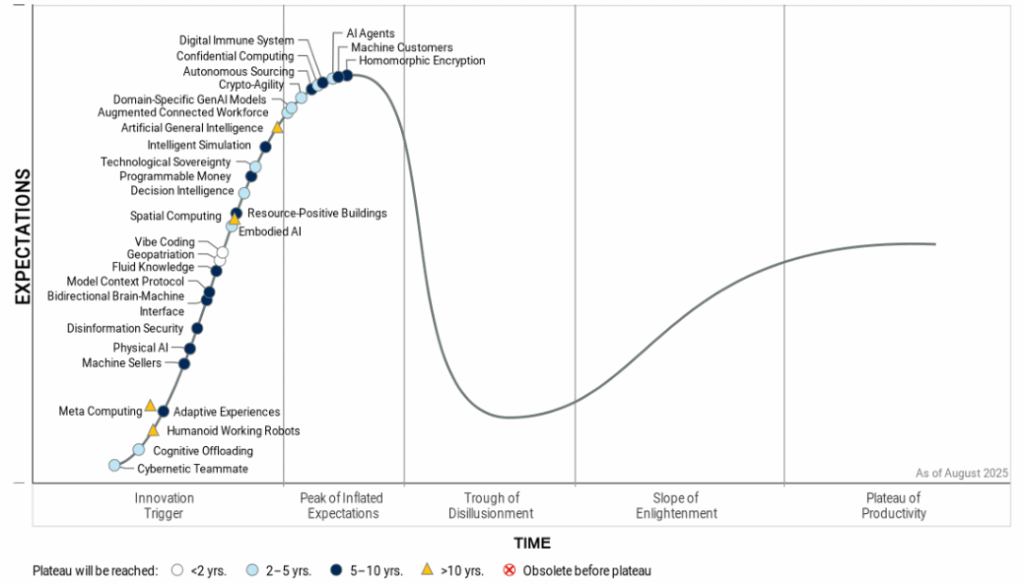
Hype Cycle for Emerging Technologies 2025
What is Data Science?
Definition:
Data science combines math and statistics, specialized programming, advanced analytics, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning with specific subject matter expertise to uncover actionable insights hidden in an organization’s data. These insights can be used to guide decision making and strategic planning.
Link: What is Data Science? | IBM
In simpler terms
– Data Science involves
- How we take data and use it to acquire
knowledge? - How we use knowledge to
- Make informed decisions
- Understand past/future trends
- Create new products/service
What is Data Mining?
Definition:
Data mining is the use of machine learning and statistical analysis to uncover patterns and other valuable information from large data sets.
Link: What is Data Mining? | IBM
What is data?
Is Data == Information?
What is Data?
Data Explosion: According to IBM, worldwide data volumes are currently doubling every two years.
▪ 1.5 billion people are active on Facebook daily
▪ Europe has more than 307 million people on Facebook
▪ There are five new Facebook profiles created every second!
▪ More than 300 million photos get uploaded per day
▪ Every minute there are 510,000 comments posted and 293,000 statuses updated
Every minute:
- Snapchat users share 527,760 photos
- More than 120 professionals join LinkedIn
- Users watch 4,146,600 YouTube videos
- 456,000 tweets are sent on X (previously Twitter)
- Instagram users post 46,740 photos
Every day:
- There are 600 million Instagrammers; 400 million who are active every day
- Each day 95 million photos and videos are shared on Instagram
- 100 million people use the Instagram “stories” feature daily
As more and more data is generated automatically, we need to find automatic solutions to turn those stored raw results into information.
- A collection in either structured or unstructured format
- Structured: data sorted into a row/column structure
- Unstructured:
- Text
- Comments and reviews on social media
- Audio signals
Example of a Dataset:
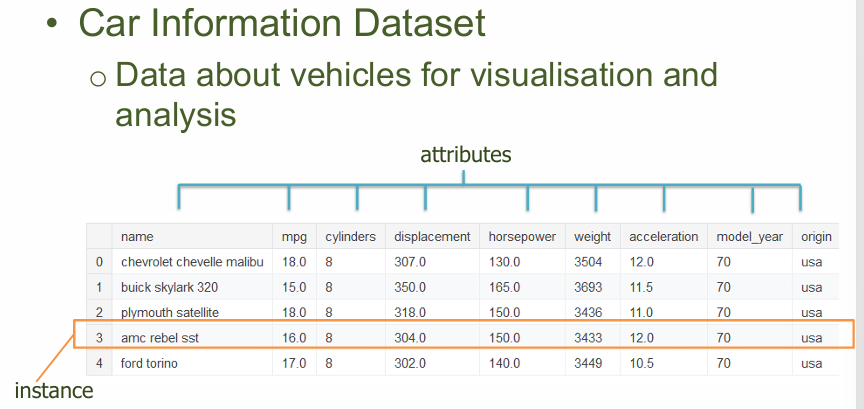
Data / Attributive Types
There are several possible types of attribute in an instance:
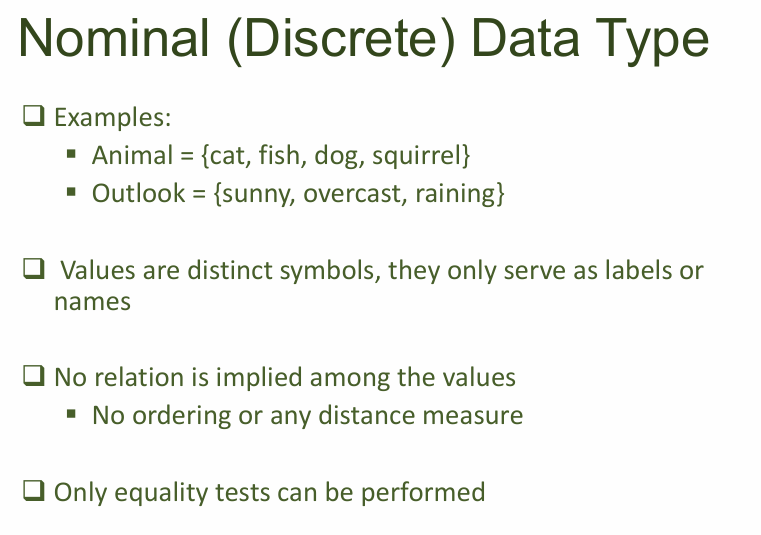
- Nominal (Discrete/Categorical)
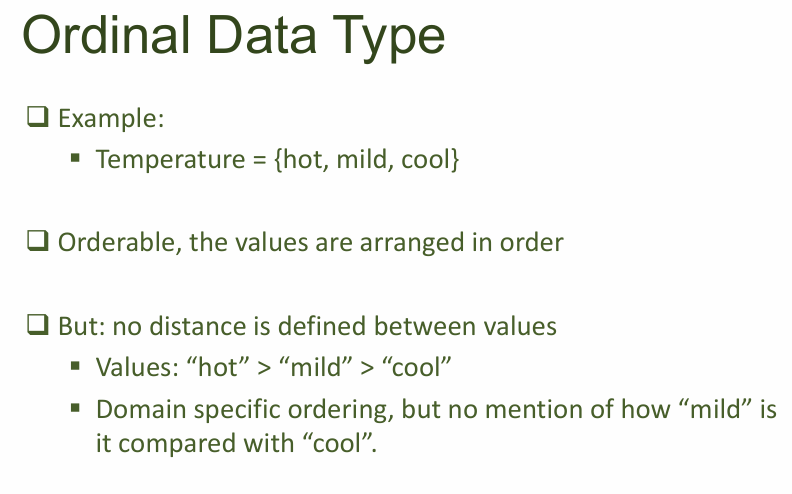
- Ordinal
- Numeric
- Interval
- Ratio
Numeric/ Continues Data type
Numeric or continuous data type can be divided into two:
▪ Interval Data Type
▪ Ratio data Type
Interval Data Type
❑Example:
▪ Year = {1990, 2000 ,1995, 2005}
▪ Year: 1990 < 1995 < 2000 < 2005
❑ Ordered but measured in fixed and equal units
❑ The difference between values make sense
▪ 1995 is 5 years after 1990
❑ But: The sum does not make sense
▪ 1990 + 1995 = year 3985!!
Ratio Data Type
❑ Example:
▪ Distance (m) = {1, 2, 3, 5}
❑Ordered, measured in fixed unit and values are relative to zero
❑The difference between values make sense:
▪ 3m is greater than 2m
❑Sum makes sense as well
▪ 3m + 2m = 5m
Q & A
- Classify the following as Ordinal or Nominal
- The origin of the beans in your cup of coffee
- The place someone receives after completing a race
- The metal used to make the medal that they receive after placing in the race
- The telephone number of a client
- How many cups of coffee you drink in a day
Conclusion;
❑Information is extracted from data
❑The main focus of data Science is finding meaningful patterns, insightful information on data, and developing some models for further analysis
❑Data types can be nominal, ordinal, and numeric