What is an Algorithm?
An algorithm is simply a set of rules for carrying out some calculation. either manually or on a machine.
Example: the most basic algorithms one can think of are those related to addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of numbers.
Types of Algorithms:
Correct algorithms:
Its output is always the correct answer to the problem.
Approximation algorithms:
Produce solutions that are close to the correct answer, often within a known error bound (e.g., decimal approximations).
Probabilistic algorithms: Produce outputs that depend on both the input and random choices made during the execution of the algorithm.
Deterministic algorithms: Produce outputs that depend solely on the input, with no randomness involved.
Heuristic algorithms: Produce solutions that may not be optimal but are acceptable or “good enough” in practice, often focusing on efficiency.
Why data structures and algorithms?
- How data are cleaverly organised and stored?
- How to write an efficient algorithm?
| Data Structures | Algorithms |
| Array, Lists | Insert |
| Stacks, Queues | Delete |
| Heaps | Find |
| Trees | Merge |
| Hash Tables | Sort |
| Graphs |
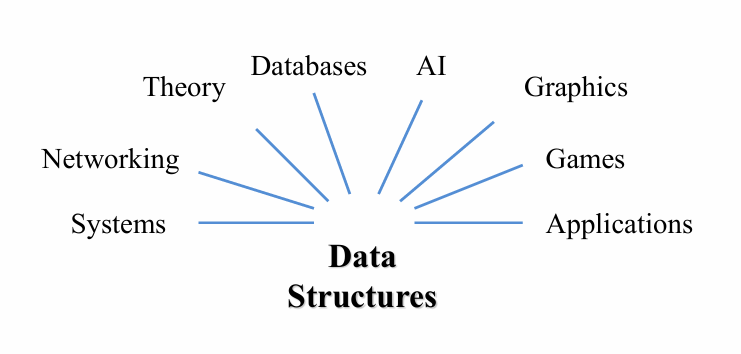
Data Structures used Everywhere!
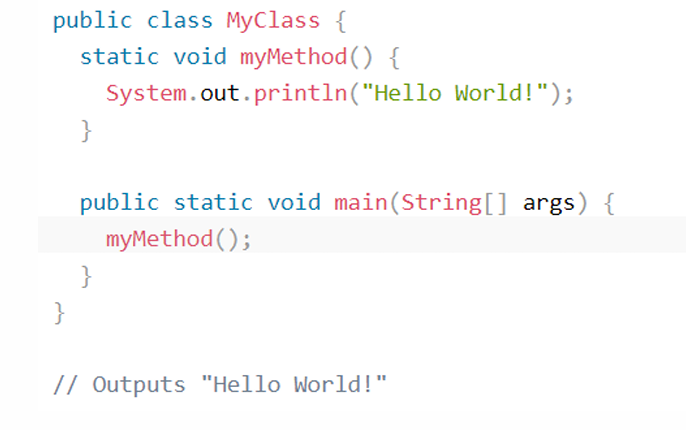
A Quick Revision: Classes and Objects

A Quick Revision: Classes and Objects
Methods are declared within a class, and that they are used to perform certain actions.
A Quick Revision: Constructor 1
- A constructor is a special method that is used to initialize objects.
- The constructor is called when an object of a class is created.
- It can be used to set initial values for object attributes.
A Quick Revision: Constructor 2

A Quick Revision: Modifiers 1
- The public Keyword is an access modifier, meaning that it is used to set the access level for classes, attributes, methods and constructors.
Modifiers are:
Access modifiers: control the access level
Public: The class is accessible by any other class.
Non-Access Modifiers: do not control level but provide other functionality.
A Quick Revision: Modifiers 2
Access Modifier for classes:
Public:
The class is accessible by any other class.
Default:
The class is only accessible by classes in the same package.
This is used when you don’t specify a modifier.
A Quick Revision: Modifiers 3
Access modifier for attributes, methods and constructors:
Public: The code is accessible for all classes
private: The code is only accessible within the declared class.
default: The code is only accessible in the same package. this is used when you don’t specify a modifier.
Protected: The code is accessible in the same package and subclasses.
A Quick Revision: Modifiers 4
Non-Access Modifiers
For classes, you can use either final or abstratct:
final: the class cannot be inherited by other classes
abstract: the class cannot ne used top create objects.
For attributes and methods
final: attributes and methods belongs to the class, rather than an object.
***End of Part 1***